Empowering Mothers: Nutritional Secrets for a Smooth Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Experience
Understanding the Nutritional Needs of Pregnant and Nursing Mothers

Assessing Dietary Requirements for Optimal Health
During pregnancy and nursing, a woman’s body works overtime to nourish both herself and her baby, calling for extra calories, protein, and key vitamins like folic acid, iron, and calcium. To support this intense nutritional demand, a balanced diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables is essential. Nursing moms, in particular, need even more calories to maintain energy and milk supply. Each woman’s nutritional needs are unique, so consulting a doctor or nutritionist can help tailor a meal plan that’s safe, satisfying, and supportive of her individual health and wellness.

The Role of Nutrition in Pregnancy and Postpartum Recovery
Good nutrition is essential for a healthy pregnancy, smooth recovery, and positive postpartum experience. It supports the baby's development, prepares the body for labor, and aids in healing and milk production after birth. Nutritious food choices boost energy, stabilize mood, and may help reduce the risk of postpartum depression. A diet rich in whole foods also strengthens the immune system, a key benefit for sleep-deprived new moms. Even small improvements in diet can make a big difference, offering lasting benefits for both mother and baby.
Breastfeeding and the Importance of a Balanced Diet
Breastfeeding requires extra nutrients to support both milk production and the mother's health. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps ensure high-quality, sufficient milk supply and sustains the mother's energy. Key nutrients like calcium, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids are especially beneficial, promoting bone health, oxygen flow, and brain development for both mom and baby. Staying well-hydrated by drinking water throughout the day is essential, as the body works tirelessly to provide the best nourishment for the baby.
Key Nutritional Strategies for a Healthy Pregnancy
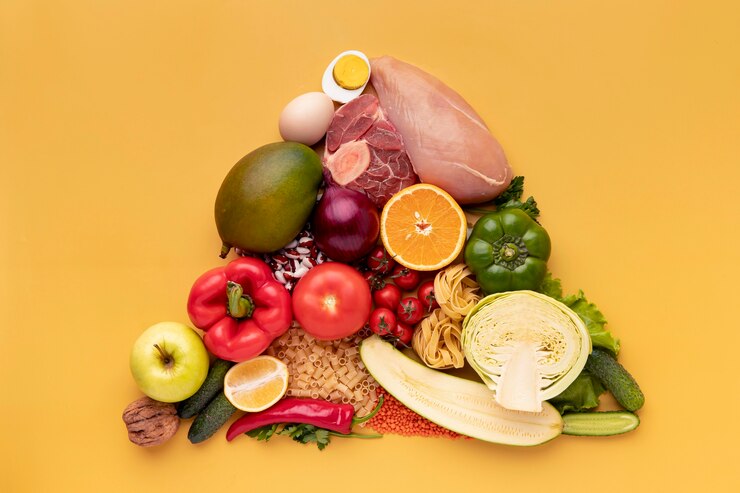
Incorporating Whole Foods and Nutrient-Rich Foods
Whole foods are essential for a healthy pregnancy, offering vital nutrients in their natural forms to support both mother and baby. A diet centered on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides a wealth of vitamins, minerals, and fiber that meet the increased nutritional demands of pregnancy. Leafy greens like spinach and kale, colorful fruits such as berries and citrus, and whole grains like quinoa and brown rice deliver key nutrients for the baby’s development and the mother's well-being. Lean proteins from chicken, fish, legumes, and calcium from dairy or fortified plant-based alternatives further contribute to a strong, balanced pregnancy diet.

Managing Weight Gain and Maintaining Healthy BMI
Healthy weight gain is essential during pregnancy, as both too little and too much can pose risks. The ideal amount depends on your pre-pregnancy BMI, with most women needing to gain between 25 to 35 pounds, though this can vary. To manage weight gain effectively, focus on regular, balanced meals with nutrient-dense foods, practice portion control, and stay active with safe exercises. Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider can help ensure that weight gain stays on track for a healthy pregnancy.
Hydration and the Benefits of Adequate Fluid Intake
Hydration is vital during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as water supports amniotic fluid formation, increases blood volume, aids digestion, and prevents constipation. For nursing moms, staying well-hydrated is key for milk production. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, and adjust intake based on activity level and climate. Signs of good hydration include clear or light yellow urine, infrequent thirst, and soft, moisturized skin.
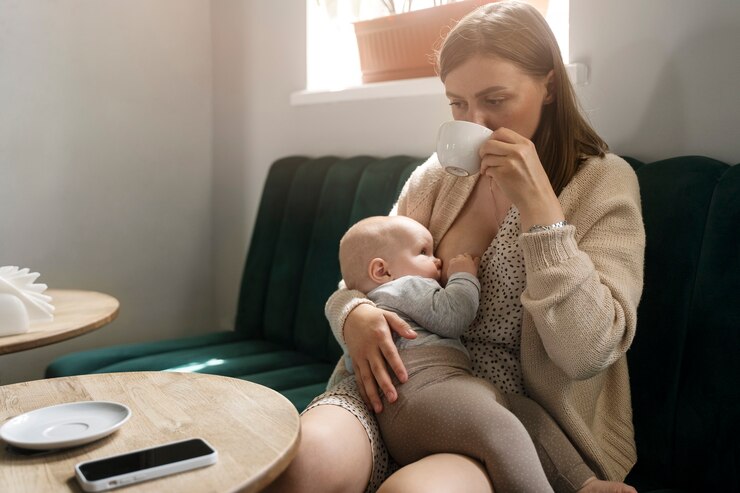

Leveraging Nutrition for Breastfeeding Success
The Importance of Nutrition in Establishing a Strong Milk Supply
A well-nourished mother is better prepared to produce abundant, nutrient-rich milk, essential for her baby’s growth and development. Breastfeeding requires more calories than pregnancy, with an additional 300-500 calories needed daily from nutrient-dense foods. Key nutrients for milk production include protein for tissue repair and growth, calcium for strong bones, iron to prevent anemia, and omega-3 fatty acids to support the baby’s brain development. This balanced diet not only boosts milk quality and quantity but also helps the mother maintain her own health and energy.
Strategies for Maintaining Healthy BMI Post-Pregnancy
Returning to a healthy weight after pregnancy is a gradual process that requires patience. Breastfeeding naturally helps burn extra calories, but a balanced diet and regular exercise play important roles too. Focus on nutrient-dense foods rather than strict calorie counting, stay hydrated to support metabolism, and ease into gentle exercise once your doctor approves. Adequate sleep helps regulate hunger hormones, and avoiding crash diets is essential to protect your milk supply. Aiming for a steady weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week is generally safe for nursing moms. Embrace your body’s changes and prioritize overall health rather than focusing solely on the scale.

Conclusion
Nourishing your body with a balanced diet and staying hydrated are fundamental for a healthy pregnancy, smooth postpartum recovery, and successful breastfeeding. Prioritizing nutrient-dense foods, safe exercise, and gradual weight management supports both maternal health and the baby’s development. Every mother’s journey is unique, so consulting healthcare providers can ensure that nutritional needs are met in a way that suits individual circumstances. Embrace the process, and remember that caring for yourself is essential to caring for your baby.